How to Make Glitch Art: Complete Beginner's Guide
Introduction
Welcome to glitch art — an exciting digital art form that transforms digital errors into deliberate creative expression. Whether you’re an experienced artist exploring new territories or a complete beginner picking up your first tool, this guide covers everything you need to start creating: the philosophy behind glitch art, its rich history, the essential tools and software, practical techniques you can try today, and how to share your work with a growing global community.
Ready to dive deeper into the fundamentals? Our dedicated What is Glitch Art? guide explores the philosophy and definitions in detail.
What is Glitch Art?

Glitch art involves intentionally manipulating digital images, videos, or audio files to introduce unexpected visual effects. Unlike traditional art forms that strive for technical perfection, glitch aesthetics celebrate imperfections and distortions — turning them into the entire point of the work.
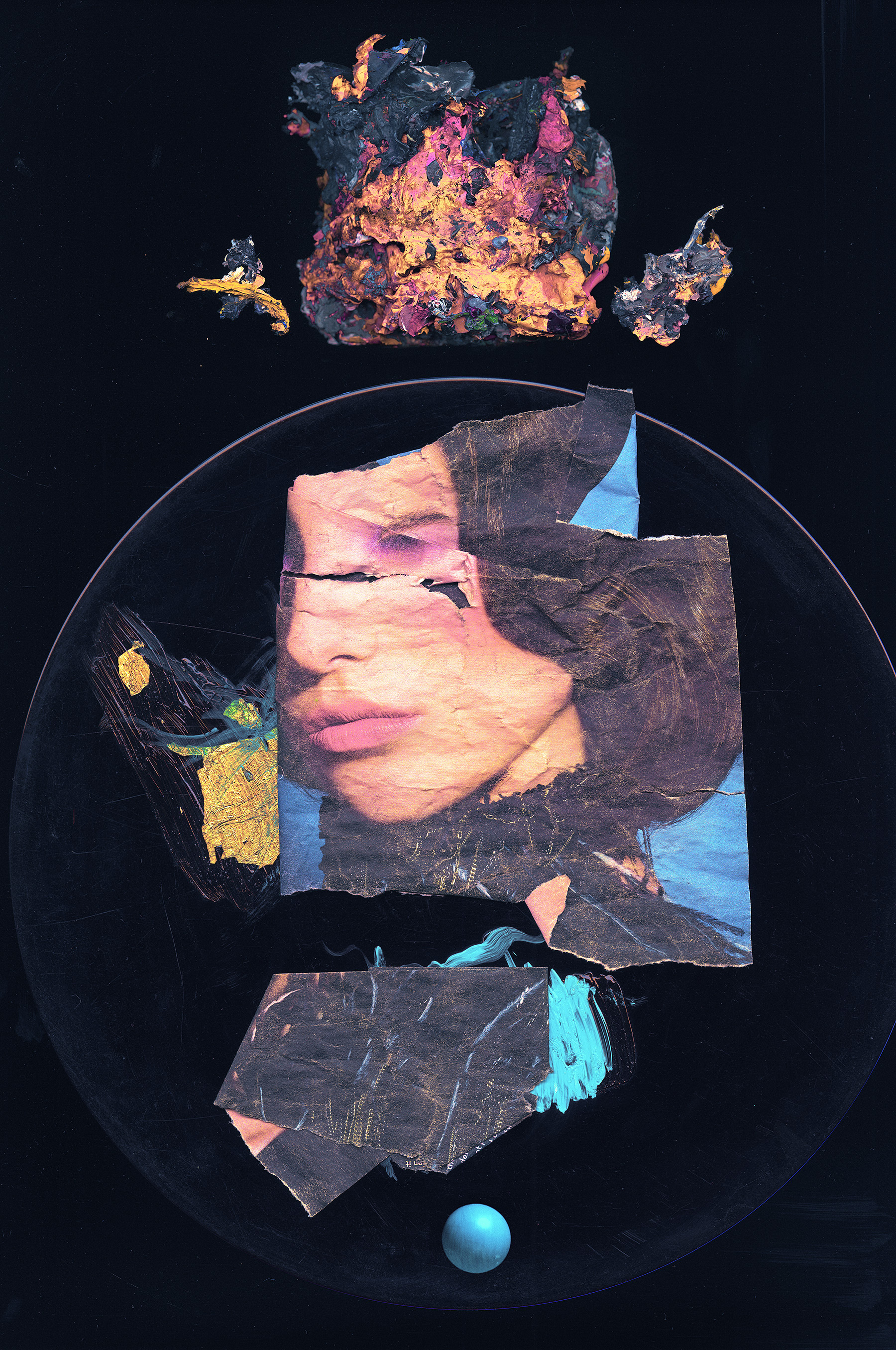

The art form leverages pixelation, color shifts, chromatic aberration, and other digital anomalies to create distinctive pieces that feel handcrafted and unique. A glitch is a hidden door to a secret world — a realm beneath conventional digital aesthetics where corrupted data reveals patterns and beauty that no algorithm was designed to produce. From subtle RGB splits to aggressive full-frame corruption, the spectrum of glitch expression is vast and continuously evolving.
Historical Development

Glitch art emerged in the 1960s and 70s when artists first began experimenting with analog technology distortions — feeding video signals through unintended circuits, manipulating cathode ray displays, and exploiting the unpredictable behavior of early electronics. The term “glitch art” itself became standard in the early 2000s as digital technology evolved and a dedicated community formed around the practice.
For a deeper look at the movement’s origins, pioneers, and evolution, see our Glitch Art History page.
Key milestones:
- 1960s: Pioneering work with analog distortion by artists like Nam June Paik and the Vasulkas
- 1990s: Internet art collectives emerged, embracing browser-based and software glitches
- Early 2000s: Datamoshing techniques gained prominence through viral videos and music videos
- Today: Dynamic exploration of new digital techniques, from pixel sorting algorithms to AI-assisted corruption, practiced by artists worldwide
Essential Tools and Software
You don’t need expensive equipment to start making glitch art. Many of the best tools are free, and the techniques range from drag-and-drop apps to deep code manipulation. Here’s a breakdown of the main categories. For a comprehensive overview, see our Glitch Software guide.
Image Editing

Adobe Photoshop remains the most widely used professional tool for image-based glitch art, offering displacement maps, channel manipulation, and raw data editing capabilities. Free alternatives like GIMP provide comparable power for pixel manipulation and color adjustments, while Pixelmator and Paint.NET offer simpler interfaces for quick experimentation. Each of these tools lets you separate color channels, apply distortions, and composite glitched layers — the core workflow for image-based glitch work.
Video Editing

For video glitch art, Adobe Premiere Pro leads the field with timeline-based effects and plugin support. Final Cut Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and After Effects all offer distinct advantages — After Effects for motion graphics and compositing-heavy glitch work, DaVinci Resolve for its powerful free tier and node-based color corruption, and Final Cut Pro for tight macOS integration. Our Video Glitch guide covers the core principles that apply across all these tools.
Code-Based Tools

Processing, Pure Data, and Max MSP enable artists to write custom algorithms that manipulate raw file data, generate visual noise, or create real-time interactive glitch performances. These environments open up possibilities that pre-built software can’t match — you can write your own pixel sorting algorithms, build audio-reactive visualizations, or create generative systems that produce unique corruptions every time they run.
Accessible Options

Mobile apps like Glitche, Decim8, and Mextures offer one-tap glitch effects that are perfect for experimentation and learning. Online tools like Photomosh and Glitchatron let you glitch images directly in the browser with no installation required. These accessible entry points are great for understanding what different effects look like before diving into more advanced tools. See our Free Glitch Tools guide for a complete list of no-cost options.
Core Techniques
Data Bending

Databending is the practice of opening a media file in software that wasn’t designed to handle it — such as importing an image into an audio editor like Audacity — then applying transformations and saving the result. The mismatch between the expected data format and the actual processing creates unpredictable visual artifacts: color band shifts, horizontal tearing, and wave-like distortions that would be impossible to achieve any other way. It’s one of the most accessible techniques for beginners because you can start with free tools and see dramatic results immediately.
Circuit Bending
Circuit bending bridges the physical and digital worlds. By physically manipulating electronic device circuits — using wires, alligator clips, or direct soldering on video mixers, old game consoles, and CRT displays — artists generate unexpected sounds and visuals directly from hardware. The results are organic and unpredictable in ways that software simulation can’t fully replicate. Always exercise caution with electronics: work with low-voltage battery-powered devices when starting out, and never circuit bend anything connected to mains power.
Code Manipulation

Code manipulation involves editing image or video file data directly, whether through hex editing (modifying raw bytes in a hex editor), writing scripts to rearrange pixel data, or building custom Processing sketches that distort visuals algorithmically. This technique gives you the most granular control over your glitches — you can target specific byte ranges to corrupt only certain color channels, or write algorithms that create perfectly repeatable effects. Hex editing is the most direct form: open any image file in a hex editor, change a few values in the pixel data region, and watch the image transform.
Pixel Sorting

Pixel sorting is an algorithmic technique where pixels in an image are selected by brightness, hue, or other criteria, then rearranged in sorted order within defined regions. The result is a distinctive streaking effect — smooth gradients of color that cascade through the image while leaving other areas untouched. Artists control the effect by adjusting thresholds, sort direction, and which pixel property drives the sort. It has become one of the most recognizable glitch art techniques, widely used in glitch photography and digital illustration.
Datamoshing
Datamoshing exploits how video compression works. Modern video codecs like H.264 store full keyframes (I-frames) and then predict the differences between frames (P-frames and B-frames). By removing or manipulating keyframes, you force the decoder to apply motion data from one scene onto the visual content of another — creating the signature “melting” and “smearing” effects where shapes ooze and bleed across cuts. The technique gained mainstream visibility through music videos and has since become a staple of video glitch art.
Generational Loss
Generational loss creates glitch effects through repeated compression cycles. Each time you save, compress, re-open, and re-compress a file, the compression algorithm introduces new artifacts and amplifies existing ones. After enough cycles, the image or video degrades into abstract patterns of macroblocking, color banding, and ghosting. It’s a meditative, process-driven technique that reveals how digital media slowly decays under its own encoding infrastructure.
Glitch Aesthetics

The visual language of glitch art encompasses a wide range of styles, each with its own character and cultural resonance. Glitch aesthetics are defined by color distortions, pixelation, datamoshing effects, and an embrace of randomness — but within that broad category, distinct movements have emerged.
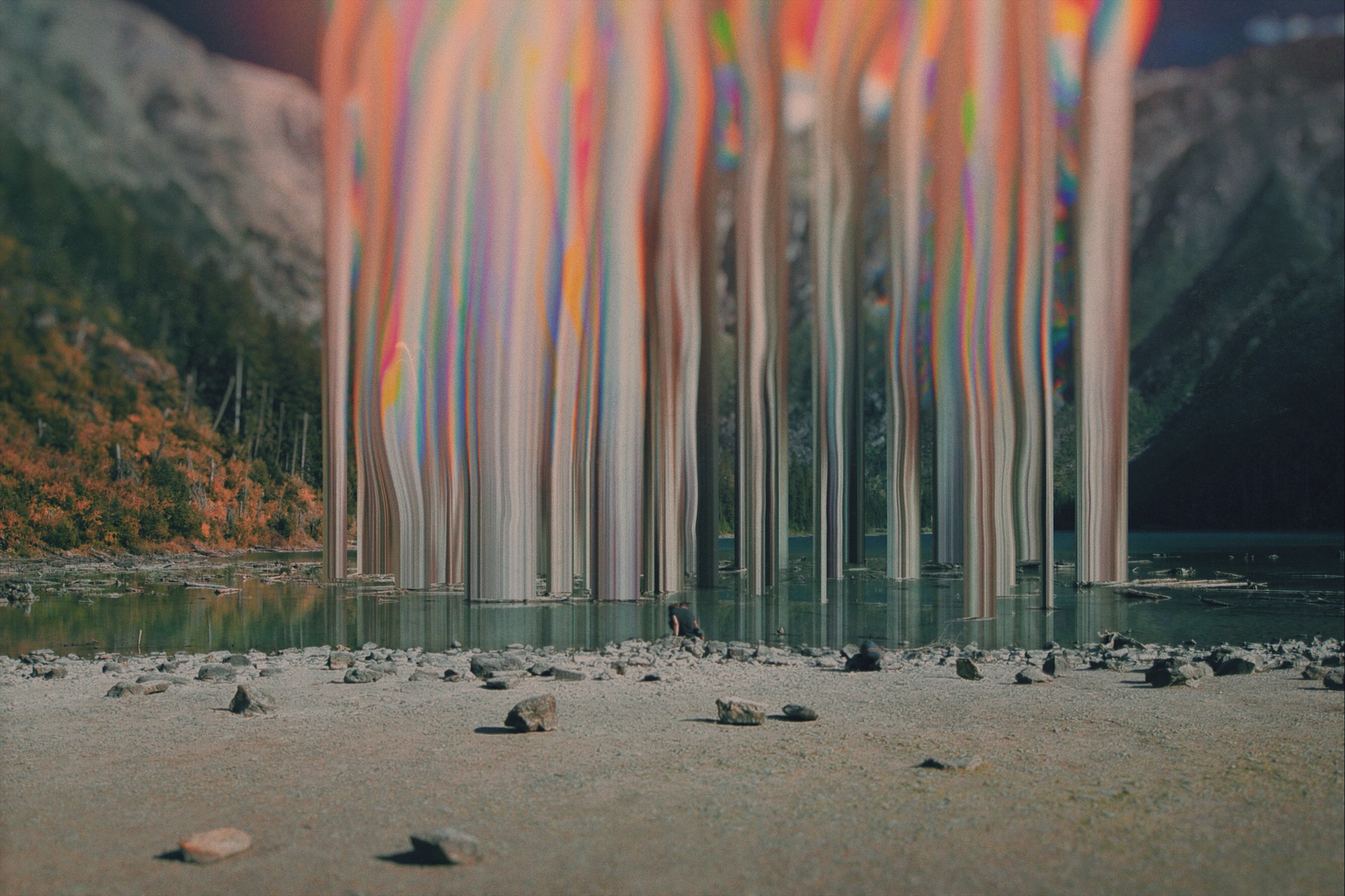

Glitchcore draws heavily on the chaotic, maximalist end of the spectrum — layered distortions, aggressive color shifts, and hyper-fragmented compositions often paired with internet culture imagery. VHS effects evoke analog nostalgia through tracking errors, scan lines, and color bleeding that recall degraded tape playback. RGB split and chromatic aberration isolate and offset color channels to create the signature red-cyan-green fringing seen in everything from movie titles to album covers. Glitch drawing and glitch typography apply these principles to illustration and letterforms respectively.
Success in glitch art comes from finding your own balance between chaos and intention — valuing imperfection over polish while still developing a recognizable aesthetic voice.
Finding Inspiration
- Explore other glitch artists’ work to understand the range of approaches and aesthetics
- Join the glitch art community through galleries, forums, and social media groups
- Document real-world glitches in technology, nature, and everyday occurrences — a corrupted billboard, a frozen video call, a misaligned print job
- Experiment across different techniques and tools — combining databending with pixel sorting, or layering VHS effects over datamoshed footage
- Draw inspiration from music, film, and literature for interdisciplinary approaches to digital disruption
Ethical Considerations
Remember to:
- Respect copyright and obtain permissions when necessary
- Consider the context and appropriateness of appropriated materials
- Secure consent when using personal or sensitive content
- Credit other artists when their techniques or works directly influence yours
Sharing Your Work
Effective platforms:
- Social media with relevant hashtags (#glitchart, #digitalart, #databending, #pixelsorting)
- Portfolio sites like Behance, Dribbble, or DeviantArt
- Local and online art exhibitions
- The glitch art community — dedicated forums, Discord servers, and subreddits where artists share work and exchange techniques
Troubleshooting
Technical issues: Save frequently and always work on copies of your source files — true glitching is destructive by nature. Clear your cache and restart if your editor behaves unexpectedly, and keep software updated for stability.
Creative blocks: Take breaks, experiment with a technique you haven’t tried before, and seek feedback from other glitch artists. Sometimes switching from image to video work (or vice versa) is enough to break through a rut.
Recreating effects: Research how other artists achieved similar results. Many techniques are documented in tutorials across the community. Start with our technique guides — databending, pixel sorting, datamoshing, hex editing — and adapt their approaches through experimentation.
Conclusion
Glitch art celebrates experimentation and imperfection. With these tools, techniques, and resources, you’re equipped to join the growing community of glitch artists and create compelling digital works that reveal the hidden beauty in digital failure.
Next Steps
Ready to go deeper? Here are the best paths forward based on your interests:
- Start creating now: Visit our Getting Started page or try the Image Glitch Tutorial for a hands-on walkthrough
- Learn a technique: Dive into databending, pixel sorting, datamoshing, or circuit bending
- Pick your tool: Explore guides for Photoshop, GIMP, After Effects, Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, Processing, or browse free glitch tools
- Find your community: Connect with fellow practitioners through the glitch art community
- Get inspired: Browse work by established glitch artists and explore the glitch art history that shaped the movement